Full Library / Resource / Event Queue / Queue_N
Block Name: Queue_N
Code File Location: VisualSim/actor/lib/Queue_N
Note: If you have purchased the Smart_Resource package, use the Smart_Resource block and not this one.
o Define multiple Ingress or Egress ports using a single block.
o Create a FIFO or LIFO with multiple concurrent queues.
o Define a temporary memory location to store requests or transactions from different sources or different destinations in separate queues.
o Create rudimentary cache with equal sized data access (Read or Write). Consider each FIFO/LIFO in the Queue_N to define a single block of cache.
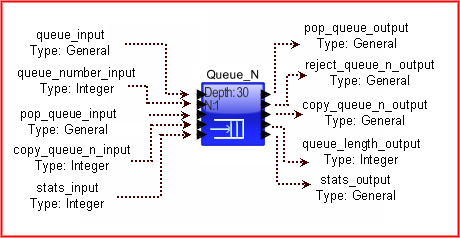
The following is a block diagram that illustrates the operation of the Queue block.
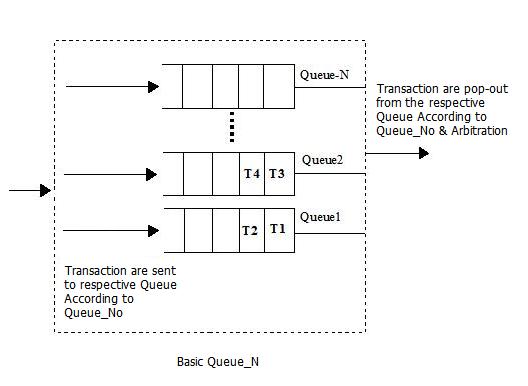
This block defines multiple queues of equal length operating as independent queues. When a transaction arrives on the input port, the transaction is assigned to a particular queue based on the queue_number_input port value. This block queues the incoming transaction or token in a FIFO or LIFO order. When the block receives a value on the pop_input port, it sends the head of the Queue on the output port. The queue_number_input port specifies the target queue to be output. If the value on the pop_input port is an integer, it sends the data structure in the specific numbered location of the queue on the output port. To queue a transaction and to pop a queue, the queue_number_input port value is required.
If the queue is full, then the incoming Data Structure or token is placed on the reject_output port.
To illustrate the usage, look at the following Examples in the BDE.
Statistics Output
Statistic Name |
Value |
Explanation |
Mathematical Equation |
Type |
Number_Entered |
100 |
Number of transactions entering the queue. |
- |
int |
Number_Exited |
25 |
Number of transactions that left the queue. |
- |
int |
Number_Rejected |
10 |
Number of transactions rejected and output to reject port . |
- |
int |
Queue_Number |
1 |
Queue Number. Queue number start at 1. |
- |
int |
Occupancy_Min |
4.0 |
Minimum queue size during the simulation. |
// Obtain Min for X, where X0 = Double.MAX_VALUE if (Xn < Xn – 1) Xmin = Xn |
double |
Occupancy_Mean |
8.0 |
Mean/Average queue size during the simulation. |
// Obtain Mean for X Xµ = (1 / n) * (X1 + X2 + … + Xn) |
double |
Occupancy_StDev |
3.0 |
Standard Deviation from the Mean queue size during the simulation. |
// Obtain Standard Deviation for X |
double |
Occupancy_Max |
25.0 |
Maximum queue size consumed during the simulation. |
// Obtain Max for X, where X0 = Double.MIN_VALUE if (Xn > Xn – 1) Xmax = Xn |
double |
Total_Delay_Min |
1.3 |
In seconds. Least time through the queue among all transactions. |
// Obtain Min for X, where X0 = Double.MAX_VALUE if (Xn < Xn – 1) Xmin = Xn |
double |
Total_Delay_Mean |
1.3 |
In seconds. Mean/Average time through the queue among all transactions. |
// Obtain Mean for X Xµ = (1 / n) * (X1 + X2 + … + Xn) |
double |
Total_Delay_StDev |
1.3 |
In seconds. Standard Deviation from the Mean time through the queue among all transactions. |
// Obtain Standard Deviation for X |
double |
Total_Delay_Max |
1.3 |
In seconds. Maximum time through the queue among all transactions. |
// Obtain Max for X, where X0 = Double.MIN_VALUE if (Xn > Xn – 1) Xmax = Xn |
double |
Utilization_Pct_Mean |
0.0 |
Not Used for Queues. Will default to 0.0. |
Where n is the number of samples and X is occupancy or delay.
Parameter |
Explanation |
Type |
Max_Queue_Length |
This is the maximum number of tokens or data structures that can be in the queue at any instance of time. This length is the same for each queue. All items above this limit will be send to the reject_output port. |
Integer |
Number_of_Queues |
This specifies the number of queues in this block. |
Integer |
Initial_Queue_State |
Queue initial state attribute. This setting is used whenever the queue is empty and the first token arrives. |
- |
Queue_Type |
Queue type attribute, either 'Queue_FIFO', or 'Queue_LIFO'. The default is 'Queue_FIFO'. FIFO means first-in-first-out, whereas LIFO means last-in-last-out. This pertains to the ordering of the incoming Data Structure in the queue. |
- |
Port |
Explanation |
queue_input |
Input port for data tokens (numerical values) or data structures entering the queue. The queues can support any token type (integers, arrays, double, strings, booleans and data structures). This input must arrive with a queue_number_input that contains the queue number to assign the incoming token or data structure. |
queue_number_input |
This is an input port that is a required to assign to a particular queue and pop from a queue. A value is required on this port for both the queue_input and pop_queue_input. |
pop_queue_input |
This port initiates the queue to send an item out of the queue. This must arrive with a queue_number_input that contains the queue number to pop the token or data structure. This input can either be an interger or any data type. If it is a non-integer data type then the head of the queue is sent to the pop_queue_output port. If the value is an integer, then the input number is the token location to be sent out. |
copy_queue_n_input |
This input specifies the index location of a token in the queue that must be placed on the 'Copy_queue_n_output" port. This must arrive with a queue_number_input that contains the queue number. The items in the queue are not disturbed, thereby preserving the queue order. This is used to trigger an algorithm like a arbiter to act on the incoming request. This copied data structure can be a request for service or access. |
stats_input |
This port is triggered to output accumulated statistics for this block. If the stats_input is a positive queue number, ranging from 1 to Number_of_Queues, the current statistics for that queue is placed on the stats_output. If the stats_input is a negative queue number, ranging from -1 to -(Number_of_queues), the current statistics are reset for the particular queue. When the statistics are reset, the Number_in_Queue is equal to the current queue length. |
pop_queue_output |
The pop data structure or token is placed on this port and the token is removed from the queue. |
reject_queue_output |
The incoming token is sent to this output if the selected queue is full. |
copy_queue_n_output |
This outputs the current token or Data Structure in the index location specified by the integer on the 'copy_queue_n_input' port and in the queue specified in 'queue_number_input' port. The data structure is not removed from the queue. |
queue_length_output |
This provides the length of the queue each time a token is received on either the input_queue, pop_queue_input or copy_queue_n_input ports. |
stats_output |
Output port receiving queue statistics as a data structure. A single queue statistics is output as a data structure while the statistics for all the queue is output as an array of data structures, where each data structure corresponds to one of the queue statistics. See top for details on the fields of this Data Structure. |
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Easily create PDF Help documents