Industry background
Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the collection of physical devices that are connected to the internet. The connection enables us to collate and share data about the devices. For example, home automation systems. The system collects data about the functioning of the air-conditioning units, refrigerators, and several other electrical and electronics appliances at home. Users can monitor the health of the systems remotely and with the collected data can also operate and take actions remotely.
The application of IoT becomes even more critical in industrial settings. They have machinery which needs to be functioning optimally at all times. Downtimes would cost a lot and an efficient maintenance mechanism is needed to prevent downtimes. At the same time, manual supervision is a cumbersome process and hence remote monitoring and maintenance become essential.
Problem
In an IoT environment, several sensors are used to collate information about the performance of physical systems. The information is then processed at a data center so as to provide actionable insights about the working of the physical systems.
The effective functioning of the IoT system is dependent on several factors such as the details of the sensors, network infrastructure, scalability of the system, and so on. Such dependencies make creating an IoT environment, especially in an industrial atmosphere costly and time-consuming. Hence to build a fool-proof mechanism, modeling of the IoT system is essential prior to the actual implementation.
Let us take the example of the IoT environment in an agricultural field. The deployed sensors measure major factors such as soil quality, atmospheric humidity, cattle health, and so on. Failure or malfunctioning of even one of the sensors may have serious repercussions on the agriculture produce and may result in a loss for the farmer and also in food scarcity as well.
Model construction
Using VisualSim, you can build a model to replicate an IoT system. An example of such an IoT model is given below.
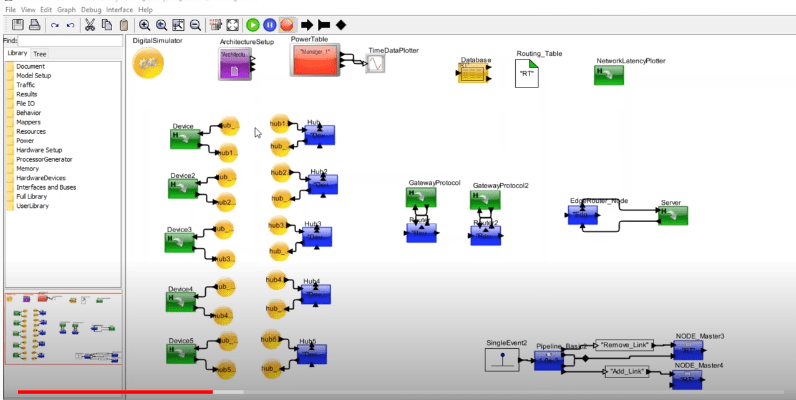
In the above model, the green blocks represent physical devices which are connected to the nodes (blue blocks). Note that the connections are based on the bandwidth. We also have routers and an edge router that is connected to a processing unit.
There is a power table that tracks the power consumed by different components and the database provides the connection details.
The main objectives of the above model are listed below:
- Selecting the right clock speed, number of cores, memory capacity, and sensor quality.
- Selecting arbitration algorithms based on priority and network efficiency.
- Partitioning applications between ASIC (cores + accelerators), processors, and FPGA.
- Measuring the architecture performance for application and workload.
- Designing of the smart hub for consolidating and processing the sensor data.
Download VisualSim Architect Click here
Types of Analysis
The analysis of the IoT model involved checking the latency of the network such as the data center latency and capturing the end-to-end latency between one node to another.
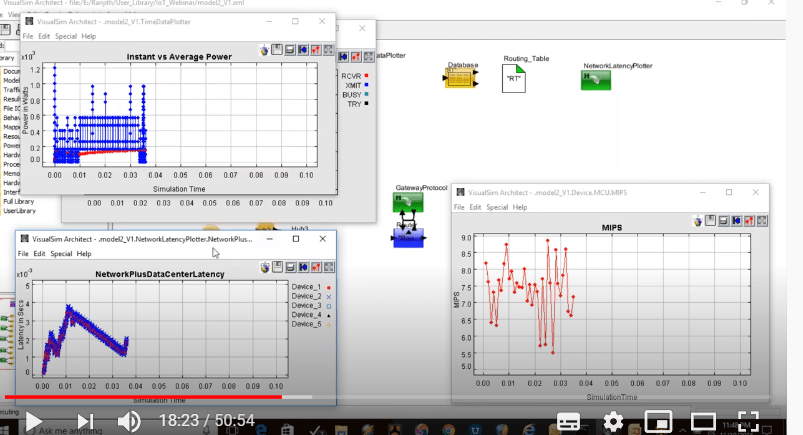
With respect to power analysis, the focus was on improving battery efficiency and extending battery life. We calculated the number of power management states and wanted to devise a mechanism to reduce power consumption based on the power management logic. In addition, details of the amount of the power that needs to be used and the impact on the battery were also calculated.
Conclusion
Based on the model, the following were the decisions taken to enhance the IoT implementation:
- Make better architectural decisions based on quantitative results, instead of guesswork.
- Use system simulation to determine the latency and power consumed of a network of IoT devices.
- Architect the hardware and software to meet the end-to-end application timing deadlines from IoT to the data center.
- Predict and eliminate possible design bottlenecks.
Download VisualSim Architect now for free trial Click here