
Developing Applications on Top of Wireless Standards
(CDMA, GSM, 3G, Wireless LAN, Bluetooth and UWB)
Once a
technology has been standardized by IEEE, ETSI, ITU or the industry consortiums,
companies providing solutions for these market have to differentiate on the
applications offered. The standard itself will be mass-produced by
the lowest cost provider. Wireless LAN technologies such as 802.11
(WiFi), Bluetooth and Ultra Wide Band (UWB) got their beginnings in providing
a wire replacement for internet access and digital data communications.
The transfer rate robustness, high performance using embedded microprocessors
and dropping price points are making these viable for audio and video applications
such as audio streaming, video conferencing, and gaming. To accommodate
the data rate characteristics as a function of distance on top of a Wireless
network, the issues associated with wireless contention from other same network
users, and the added functionality of audio or video processing must be evaluated.
Evaluating such applications are not simply an issue of analyzing the hardware or software platforms. The network and protocols impacts can be drastic in such issues are fragmentation, network latency, throughput, contention and time-jitter. Moreover the protocols requirements must be consolidated with the hardware and software of the application.
This example considers a set of applications running on top of a Wireless LAN system. The Wireless LAN protocol is based on the model that is also available from the demonstration page. Please refer to the Wireless Example System for more details on the Wireless LAN protocol modeling. The model has the hardware-software defined at only the Access Point. The current model can be easily modified to add any application-specific instructions. Moreover the protocols can also be replaced with any other standard.
The application has an Instruction Set with four (4) instructions- Read, Write, Block and Non-Block. The instructions can be executed on a µProcessor or custom ASIC. Both of these solutions require access to the Cache and memory. The ASIC and µP has been modeled separately to accommodate for on-chip cache modeling. The flow of data is similar for both the ASIC and µP flows as shown below:
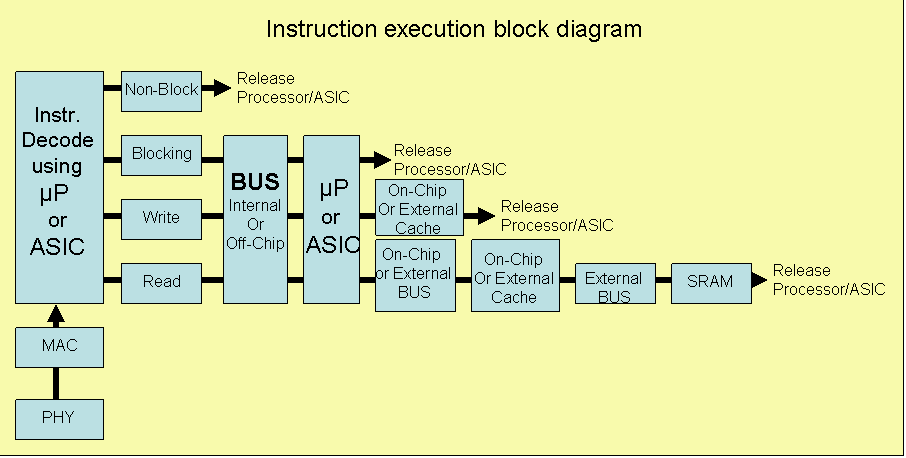
Model Applets: The VisualSim model of the application processing flow diagram shows the behavior mapping to the platform resources. These resources can be on-chip or discrete components. Modifying the parameters provides the specific implementation.
Evaluating such applications are not simply an issue of analyzing the hardware or software platforms. The network and protocols impacts can be drastic in such issues are fragmentation, network latency, throughput, contention and time-jitter. Moreover the protocols requirements must be consolidated with the hardware and software of the application.
This example considers a set of applications running on top of a Wireless LAN system. The Wireless LAN protocol is based on the model that is also available from the demonstration page. Please refer to the Wireless Example System for more details on the Wireless LAN protocol modeling. The model has the hardware-software defined at only the Access Point. The current model can be easily modified to add any application-specific instructions. Moreover the protocols can also be replaced with any other standard.
Model Overview
A behavior block called Mapper_Adv has been added at the top-level for the Access_Point. This block transfers the request in the form of an incoming Data Structure to the associated HW_SW_Proc resource block just above. The communication is made through the Virtual Connection capability of VisualSim. The application execution resource has been modeled as a hierarchical block. The resource is shown in the second Applets.The application has an Instruction Set with four (4) instructions- Read, Write, Block and Non-Block. The instructions can be executed on a µProcessor or custom ASIC. Both of these solutions require access to the Cache and memory. The ASIC and µP has been modeled separately to accommodate for on-chip cache modeling. The flow of data is similar for both the ASIC and µP flows as shown below:

Modifying Parameters to create new scenarios
All the parameters available from the Wireless LAN System are available in this model. This includes frame size, fragmentation limit, node frequency, DIFS and SIFS delays, traffic rate and Frame_Size_Bytes. In addition, the following are available in the HW_SW_Proc block:- Clock rate for µP, ASIC and Bus
- Cache-hit ratio
- Cache Word size
Analysis
Three analysis graphs are displayed on this page below.- The timeline plot titled Processor States displays the period of time that the processor or ASIC is active. If the user zooms into the region around one of the red lines, you will notice that there is some intermittent processing.
- Frame Latency shows the variation of the latency against network effects and application processing as the latency is computed at the end of the application. Vary the processor or Bus speed to see the latency get modified.
- Access Out text display shows the statistics associated with the µP, ASIC, Bus, Cache, memory and system FIFO Queues.
Model Applets: The VisualSim model of the application processing flow diagram shows the behavior mapping to the platform resources. These resources can be on-chip or discrete components. Modifying the parameters provides the specific implementation.