Memory / Memory_Controller
Block Name: Memory_Controller
Code File Location: VisualSim/actor/arch/Memory/Memory_Controller
Table of contents
- Block Description
- Operation
- Timing definitions and Estimated timing for each action
- How to connect
- Expected fields and fields modified by the controller
- List of models
- Parameter configuration and ports
- How to configure (LPDDR3 and DDR4 example)\
- Power Configuration
- Enabling plots
- Statistics
- Checklist before running the model
- Deadlock and debugging
- Error messages and solutions
- Future Implementation
Description
This block emulates the memory controller operation for different types of memory technologies. It will control a DRAM device by sending the necessary commands as per the JEDEC/JESD standard. This block requires a detailed configuration of the DRAM as per the datasheet or a custom design with a proper timings.
(**By default it uses open page policy)
Operation
Internal Operations of Memory
controller:
- Address Decoding
- Scheduling
- Issue
- Buffering and response
Input request (read/write) to a
specific address have to be decoded to determine the Bank, Row and column
information.
The parameters Memory Row,
Memory Bank and Memory Column are used for this purpose.
Following
fields will be added for each request to DRAM.
A_Address_Bank
A_Address_Row
A_Address_Col
A_Address_Rank
If the memory
column is conigured as {{0,2},{4,10}}, then the total bits are
considered as 10 and the MSB is made up of {0,2}
Decoded packet will be fragmented into a single or multiple packets as per the request size. The DRAM can accept request size of Burst Length, the request greater than this will be fragmented.
The Address decoder maintians a single entry buffer to accept packet from the bus interface and it will forward the packet to the appropriate command queue if space is available.
if there is no
space in the appropiate command queue, then the requested packet will
be held in address decoder until the flow control triggers the decoder.
if the flow control is enabled at the bus interface the back pressure will be applied from memory if the previous packet is held in the address decoder.
if flow control is disabled then the incoming request will be dropped if the address decoder is occupied with the previous request.
Case
1:
Request size,
and
the Memory controller configuration is
Memory_Width_Bytes = 1
Burst_Length = 8
The input packet will be fragmented into 8 packets
Case
2:
Request size, A_Bytes = 8
and
the Memory controller configuration is
Memory_Width_Bytes = 2
Burst_Length = 8
The fragmenter will package it in a single request.
The controller will
prefetch 16 bytes of data through a single burst. The required 8 bytes
will be transfered to the source and the 16 bytes will remain buffered
in the memory controller untill the new request to
different address is
issued. The buffered data can be utilized if the next request is
sequential and 8 bytes.
The
Memory controller handles the activation and read /write access as per
the JEDEC standard.
The scheduler runs on a independent clock in which it can schedule maximum of 1 activate command and 1 memory access command to DRAM. But only one commands will be issued to DRAM. Multiple ready to issue commands will be sequentialized with 1 command per cycle.
Scheduler Selection algorithm - FR FCFS (First Ready - First Come First Serve)
1. Activates selection: (Please read activates selection restriction)
i. Select activates that are for
closed bank (No active pages) in arrival order
ii. If nothing found, select activate for different
bank goup or different banks compared to previous selection in arrival
order
a. Select a bank that doesnt have pending memory
access to the open page.
iii. If nothing found, select activate for same bank group
or same bank in arrival order
a. Select a bank that doesnt have pending memory access to the open page.
2. Memory access selection: (Please read memory access selection restriction)
i. Select sequential command to different bank
group or different bank in arrival order
ii. If nothing found, select sequential command to
same bank group or same bank in arrival order
iii. If nothing found, switch the command if queue contain alternate command
i. A read request will be bypassed if all the following condition is satisfied.
a. Request size is less than burst size
b. Previous read's request size is less than burst size and it is read from DRAM.
c. The read
data is still in the Memory controller IO buffer (Not overwritten or
discarded by any other command).
d. The Requesting column is not overlapped with the previous read and the requesting data range is available in the buffer.
4. Rescheduling cases:
i. Selected Bank is in Refresh
ii. Selected command's estimated completion overlaps with the Refresh period.
5. Scheduler Idle cases:
i. If a memory access command is scheduled but not issued yet, no new memory access command will be scheduled.
ii. If a activate command is scheduled but not issued yet, no new activate command to other banks will be scheduled.
iii. If both memory access and activate is non schedulable the scheduler goes to idle.
iv. If All bank refresh is in process.
6. Activates after refresh:
i. All bank refresh - previously openned bank
will be activated one after another with RRD timing constraint. during
this time the memory access can be scheduled to an open bank, but new
activate from the command queue cannot be scheduled. (Currently FAW
restriction does not apply)
ii. Per bank refresh and Same bank refresh -
activates will scheduled based on the requests in command queue. if
there is no request for the banks that were previously openned, then those banks will be remained
close until a request comes to the memory. (FAW restriction applies)
Note: Activate selection restriction
1. if the selected bank's estimated activation
overlaps with the refresh period the bank will be skipped in that
cycle.
2. Read activates will be giver priority first, once the number of activate to same command reahes "Commands_in_a_Row" count the scheduler switch the priority to write. Same condition applies to write activates.
3. if 4 activates is issued within the FAW window the next activate will not be issued within the same FAW window. it will be scheduled in the next FAW window.
4. if a timing constraint for a scheduled activate is not met yet, then the next activate will not be scheduled until the previous activate is issued to DRAM.
5. if the selected activate is for a open bank, then activate will be issued once RP is completed. RP and RCD must be issued back to back. No other activates will be scheduled until the activate is issued to DRAM
6. if all bank refresh is completed, the bank activate will be issued to the banks (RRD constraint applies) that were open at the time of refresh . During this activation the command queue will not be checked for activation.
7. if all bank refresh is in process, the scheduler will goe to idle and no other commands will be scheduled.
Please check the timing constraints for the activate commands
Note: Memory access selection restriction
1. if the selected command's estimated access overlaps with the refresh period the command will be skipped in that cycle.
2. Read access will be given priority first, once the scheduled reads reaches the "Commands_in_a_Row" count the scheduler switches priority to write. Same condition applies for write commands.
3. Scheduler will select commands based on the availability even if the command count does not reach the "Commands_in_a_Row" count.
4. On a read command schedule followed by a write command, the scheduler waits for the previous write to complete before scheduling the read.
5. if a read command request size is less than burst
size and the previous read is also less than burst size it is eligible
for bypass if the column does not overlap. In this case the command will not be sent to DRAM for prefetch,
but it will be bypassed to read the memory controller IO buffer.(Please
check Bypass mechanism in memory controller)
Please check the timing constraint for memory access schedule
Timing constraints for Activates:
1. Activate to a closed bank:
If it is a very first activate to DRAM - No timing constraint
Else the RRD must be maintianed before issuing the RCD command
2. Activate to an open bank:
i. Previous command is read:
RP command must be issued to close the bank, but RTP must be maintained from the previous read command. Once RTP is met the RP command can be issued to DRAM.
Once Precharge is completed theRCD can be issued immediately.
ii. Previous command is write:
RP command must be issued to close the bank, but WR must be maintained from the previous write command. Once WR is met the RP command can be issued to DRAM.
Once Precharge is completed the RCD can be issued immediately.
Note:
*For an RP to issue the RAS must be maintined along with the RTP or WR. The RAS must be maintained from the previous RCD command to the same bank in DRAM.
*If there are 4 activates within the FAW window, the next activate must wait for the current FAW window to over.
Timing constraints for Memory access commands:
1. Sequential Read/write:
If it is a very first access to DRAM - No timing constraint.
Else the CCD must be maintained before issuing the Read or Write (CAS command)
2. Read to write switch:
The Write
command will be issued after the specific timing constraint from
previous read. This restriction time varies for certain DRAM types. But
in general it will be
(Burst_length/2) cycles for DDRs.
3. Write to Read switch:
The Read command must wait for the previous write to complete. Once the write is completed, the WTR must be maintained before issuing the Read command to DRAM.
NOTE:
The response for a read request will be issued after the 1st word read
through the DRAM channel and the remaining words are processed
internally. Response for a write request will be issued out only after
all the words are written in the memory (last word out).
The Issue will send out the ready to issue commands that are scheduled by the scheduler. It will issue only one command per cycle, if there are multiple scheduled command ready to be issued, it will give priority to memory access commands and the activate will be Issued in the next cycle.
The Read response from DRAM updates the memory controller IO buffer. if the Memory is configured to send the First word out, then it will send the response in the bus interface as soon as the first word is read otherwise it will send the response once the last word is completed.
The Write response will discard the content in IO buffer and sends the response in the bus interface.
If the read request is a bypassed packet from the scheduler the data from the IO buffer will be utilized and the read response will be sent after 1 cycle.
NOTE: The response for a read request will be issued after the 1st word read through the DRAM channel and the remaining words are processed internally. Response for a write request will be issued out only after all the words are written in the memory (last word out).
Standard Timing Definitions (DDR4 values in ns)
tRRD_L Timing: 4.9 tRAS to tRAS delay
tRRD_S Timing: 2.5 tRAS to tRAS delay
tCCD_L Timing: 5.0 tCAS to tCAS delay
tCCD_S Timing: 2.5 tCAS to tCAS delay
tCL Timing: 13.75 tCAS read latency
tRCD Timing: 13.75 tRAS to tCAS Delay
tRP Timing: 13.75 Row Precharge time
tRAS Timing: 32 RCD to Precharge time
tAL Timing: 0 Additive Read/write Latency
tCWL Timing: 12.5 tCAS Write Latency
tWTR_L Timing: 7.5 Write to Read delay
tWTR_S Timing: 2.5 Write to Read delay
tWR Timing: 7.5 Write Recovery time
tRTP Timing: 7.5 Read to Precharge time
tFAW Timing: 7.5 Four Activation Window
DQSS Timing: 0 Bidirectional Data Strobe
DQSCK Timing: 0 DQS transition skew to clock
tRC tRAS + tRP
NOTE:
1. CCD timings have a restriction on the minimum value, if the
configured value is less than the burst length , the memory controller
uses the expected minumum value instead of the configured CCD value.
for DDR memories the CCD must be greater than or equal to (Burst
Length/2).
2. The response for a read request will be issued after the 1st word read through the DRAM channel and the remaining words are processed internally. Response for a write request will be issued out only after all the words are written in the memory (last word out).
Activation to a idle bank:
Generic Timings: tRCD + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel).
Activating a new Row in a bank:
Generic Timings: [tRAS | (tRTP or tWR)] + tRP + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel).
Activating a new Row in different bank and different Bank group:
Differnt bank (Closed bank) : [ tRRD | tRC ] + tRCD + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel).
Differnt bank (Open bank) : [ tRRD | tRAS | (tRTP or tWR) ]+ tRP + tRCD + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel).
Same bank (Closed bank) : tRC + tRCD + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel).
Same bank (Open bank) :[ tRAS | (tRTP or tWR) ]+ tRP + tRCD + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel).
(Applicable only for DDR4, DDR5 and LPDDR5)
Different bank group (closed bank) : [ tRRD_S | tRC ] + tRCD + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel).
Different bank group (open bank) : [ tRRD_S | tRAS | (tRTP or tWR) ]+ tRP + tRCD + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel).
Same BG Differen bank (closed bank) : [ tRRD_L | tRC ] + tRCD + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel).
Same BG same bank (closed bank) : tRC + tRCD + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel).
Same BG different bank (open bank) : [ tRAS | (tRTP or tWR) ]+ tRP + tRCD + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel).
Same BG same bank (open bank) : [ tRAS | (tRTP or tWR) ]+ tRP + tRCD + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel).
Consecutive Read or Write:
Generic Timings: tCCD + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel)
(Applicable only for DDR4, DDR5 and LPDDR5)
Different bank group : tCCD_S + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel)
Same bank group : tCCD_L + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel)
Read to Write or Write to Read:
Generic Timings
Read to Write : BL/2 + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel)
Write to Read : Write completion + WTR + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel)
(Applicable only for DDR4, DDR5 and LPDDR5)
Different bank group : Write completion + WTR_S + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel)
Same bank group : Write completion + WTR_L + (tRL or tWL) + Data transfer time (through channel)
Multiple activation are restricted by the tFAW limit. if there is a 5th request for a new activation the with in the tFAW window, the 5th request will be issued in the next window.
How to Connect Memory Controller to HW_DRAM Block
Left-Hand Side Input/Output to Memory Controller, typically from/to bus
Right-Hand Side Input/Output to HW_DRAM
Note port names in diagram
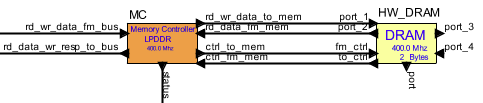
The
below image shows the proper connection of the memory controller with
the bus. The bottom two ports are dedicated for debugging and analysis.
Expected Data Structure
|
Data Structure Field |
Value (Data Type) |
Explanation |
|
A_Bytes
(necessary) |
100 (positive integer) |
This is the total bytes to be transfered for this transaction.
All bursts of this transaction will have this value. |
|
A_Command (necessary) |
"Read" or "Write" (String) |
This determines the operation. |
|
A_Address (necessary) |
100L (Long ) |
This will be used by the address decoder to determine Row, Column, Bank and Rank to perfrom the Read/Write operation. |
|
A_Source
|
"Processor" (String) |
This is unique name of the Source. When the transaction returns from the Destination, the Source and Destination names are flipped. So, the Source becomes the Destination and Destination becomes Source. |
|
A_Destination |
“DRAM” (String) |
Final Destination |
Packet Format
|
Description |
A_Command |
A_Bytes |
A_Bytes_Remaining (optional) |
A_Bytes_Sent (optional) |
|
100 Byte Read at Slave. Bus Width = 4 |
Read |
100 |
96 |
4 |
|
100 Byte Read Return at Master |
Write |
100 |
0 |
100 |
|
100 Byte Write at Slave |
Write |
100 |
0 |
100 |
What Processor_DS Fields to set for the Memory Controller
Note MC column with "User" can be set externally, "Internal" used by MC.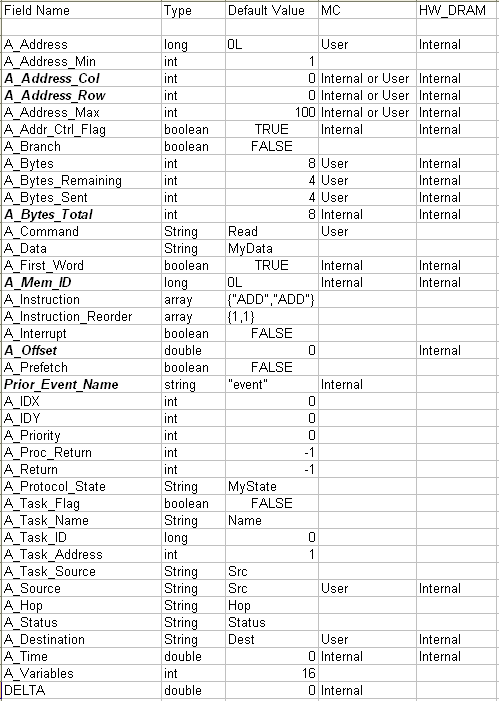
List of models
VS_AR\demo\HAL\Complex_System- Using_Mem_Controller_and_HWDRAM.xml
- Multi_AXI_to_Memory_Access.xm
VS_AR\demo\HAL\Memory_Controller
- Dual_Channel_DDR.xml
- Template_Model.xml
- Using_Memory_Controller_and_HW_DRAM.xml
Parameter Configuration
| Parameter |
Explanation | Example |
| Controller_Name | Name of this Memory Controller. This is a unique name in the entire model. | "DDR_Controller" /* DDR4 typical shown */ |
| DRAM_Type | Determines the DRAM type so that the memory controller can send appropriate commands to DRAM. | "DDR4" /* SDR, DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, DDR5, LPDDR, LPDDR2, LPDDR3, LPDDR4, LPDDR5 */ |
| Controller_Speed_Mhz | Speed of this controller in Mhz. It determines the scheduling and issue rate to DRAM. (it can be different from DRAM data rate) |
3200.0 /* DDR4 typical */ |
| Memory_Width_Bytes | Determines the word size in memory. (x8 - 1 Byte, x16 - 2 Byte, x32 - 4 Byte) |
1 /* DDR4 typical */ |
| Burst_Length | Determines the number of bursts that will be prefetched through a single command. |
8 /* 2, 4, 8, 16 DDR4 typical shown */ |
| Command_Buffer_Length | Determines the size of command queue. Array of 2 integer defines a split queue for Read and Write. Single integer defines the unified queue which can hold both Read and Write in single queue but maintian equal space for read and write. |
{160,160} /* Split Queue {Read, Write} - {32,32}*/ /* Unified Queue(Read and Writ)e - 64 |
| HW_DRAM_Name | Name of the DRAM block that is connected to this memory controller. | "DRAM" |
| Memory_Column | It defines the specific or range of bits/pins used for defining the total columns. The format is {start_bit, End_bit} It will be used for address decoding. |
{4,13} /* DDR4 typical shown */ /*{{4},{6,13}}*/ |
| Memory_Row | It defines the specific or range of bits/pins used for defining the total rows. The format is {start_bit, End_bit} It will be used for address decoding. User should make sure the bits are not overlapped with Column,Rank and Bank. |
{14,29} /* DDR4 typical shown */ /*{{5},{14,29}}*/ |
| Memory_Bank | It defines the specific or range of bits/pins used for defining the total banks. The format is {start_bit, End_bit} It will be used for address decoding. User should make sure the bits are not overlapped with Row,Rank and Column. |
{0,3} /* DDR4 typical shown */ /*{{0},{2,3}}*/ |
| Number_of_Bank_Groups | it will configure the memory organization as bank groups. Each bank group will be subdivided into set of banks. (applicable only for DDR4, DDR5 and LPDDR5) |
2 |
| Memory_Rank | It defines the specific or range of bits/pins used for defining the total ranks. The format is {start_bit, End_bit} It will be used for address decoding. User should make sure the bits are not overlapped with Row,Bank and Column. |
{30} |
| Number_of_Ranks | Currentrly not used. it will be supported in future | 2 |
| Mfg_Suggest_Timing | Array of timing, based on tCL, tRCD, tRP, tRAS. Consistent with JEDEC JESD 209 standard. The recommended timing for the DRAM as an array of six double values (in nano sec) . These six entries refer to the following settings, in this order: tCL - tRCD - tRP - tRAS - tAL - tCWL.
| {13.75, 13.75, 13.75, 32, 0, 12.5} /* tCL, tRCD, tRP, tRAS, tAL, tCWL in ns*/ /* DDR4 typical shown */ |
| Extra_Timing | Extra
timing for Memory Controller. Array of 9 added timing values:
DQSS, tWTR, tCCD, tRRD, tWR, tDQSCK, tTRP, tHWpre, tFAW to further refine
memory timing. This
is an array of additional parameters used by vendors to describe other
intermediate latencies. The format is an array of double values in ns. DQSS is the time for the BiDirectional bus strobe. tWTR is the minimum time interval between end of WRITE and the start of READ command. tCCD is the minimum time interval between two sequential reads./writes. tRRD is the minimum time interval between successive ACTIVE commands to different banks. tWR is minimum time interval between end of WRITE and PRECHARGE command. tDQSCK is the data queue strobe clock. tRTP is Read to Precharge timing. tHWpre can be used to add cycles to tRAS, tRTP, tWR parameters, default is 0. tFAWis the time period in which only 4 activates can be issued. if 5th activate needs to be issued, it must be issued in the next FAW window | {0, 7.5, 0, 0, 15, 0, 7.5, 0, 21} /* DQSS, tWTR, tCCD, tRRD, tWR, tDQSCK, tRTP, tHWpre, tFAW in ns*/ /* DDR4 typical shown */ |
| DDR4_Timings | Defines the timing information for DDR4, DDR5 and LPDDR5. CCD_L - CCD long defines the CCD between sequential access that goes to same bank group CCD_S - CCD Short defines the CCD between sequential access that goes to different bank group RRD_L - RRD long defines the RRD between activates that goes to same bank group RRD_S - RRD Short defines the RRD between activates that goes to different bank group WTR_L - WTR long defines the WTR between end of write to start of read that goes to same bank group WTR_S - WTR Short defines the WTR between end of write to start of read that goes to different bank group | {5.0,2.5,4.9,2.5,7.5,2.5} /* CCD_L, CCD_S, RRD_L, RRD_S, WTR_L, WTR_S in ns */ |
| Commands_in_a_Row | Maximum number of Read/Write sequential to be searched and transfered from the command buffer before switching to the other type of command. If parameter is greater than Command_Buffer_Length, then disables this feature. | 8 /* DDR4 typical */ |
| DRAM_Return_Cycles | Extra hardware cycles before the Read data is sent back to the bus. | 0 |
| Power_Manager_Name | Name of the power manager. "none" will disable the power. Valid PowerTable name will enable the power. | "none" /* Default */ |
| DEBUG | Enable or disable the debug option | true |
| Number_of_samples |
It defines the number of statistics to be generated for memory controller and DRAM. |
10 |
| WriteStats_to_File |
by setting true, statistics will be written in a file for memory controller.. |
true |
| Architecture_Name | The name of the ArchitectureSetup that this block is associated with. If the Architecture_setup is not available, a error will be thrown. | "Architecture_1" |
| Port | Explanation |
| rd_data_fm_mem | Read data is returned from the DRAM on this port. |
| ctrl_fm_mem | Control signals (tRAS, tRP, tRCD) returned from the DRAM on this port. |
| rd_wr_data_fm_bus | Read request and write data are sent on this port from the bus. |
| rd_wr_data_to_mem | Bi-directional port to the memory. |
| ctrl_to_mem | Control signals (tRAS, tRP, tRCD) to the memory. |
| status | status port used to send messages when DEBUG is true. |
| rd_data_wr_resp_to_bus | Read data and write acknowledge are sent on this port to the bus. |
How to Configure
The user has to extract the following timing values from the LPDDR3 datasheet:The timing values must be choosen according to the data rate.
LPDDR3:
In this configuration we are going to use 1600 data rate and a single channel 4 GB LPDDR3.
Controller_Speed_MHz : 1600.0 (1.25e-9 clock time)
Burst_Length : 8 (8n prefetch)
Memory_Width_Bytes : 4 (x32 device)
Mfg_Suggest_Timing : {15, 18, 18, 42, 0, 7.5} /* tCL, tRCD, tRP, tRAS, tAL, tCWL in ns*/
Timing_Description:
CL or RL = 12 clocks = 15ns
RCD = max(18ns,3clk) = 18ns
RP = max(18ns,3clk) = 18ns (per bank refresh)
RAS = max(42ns,3clk) = 42ns (RAS_min)
AL = 0 (choosing 0 additive latency, users choice)
CWL or WL = 6 clocks = 7.5ns
Extra_Timing : {1.25, 7.5, 5, 10, 15, 0, 7.5, 0, 50} /* DQSS, tWTR, tCCD, tRRD, tWR, tDQSCK, tRTP, tHWpre, tFAW in ns*/
Timing_Description:
DQSS min = 0.75 clock
DQSS max = 1.25 clock
we have to use 1 clock for all LPDDRs to maintain the same functionality, so 1.25ns
WTR = max(7.5ns, 4clk) = 7.5ns
CCD = 4 clocks = 5ns
RRD = max(10ns, 2clk) = 10ns
WR = max(15ns, 3clk) = 15ns
DQSCK = 2ns (DQSCK min) (applicable only for LPDDRs, for DDRs it must be 0)
RTP =max(7.5ns, 4clk) = 7.5ns
HWpre = 0 (not used in the current version)
FAW = max(50ns,8clk) = 50ns
Memory_Column : {3,12}
Memory_Row : {13,26}
Memory_Bank : {0,2}
Memory_Rank : {30}
Address_Mapping:
8 banks - 3 bits to address it.
1K Columns - 10 bits to address it
16K Rows - 14 bits to address it
Bank interleaved addressing format
| 0 to 2 | 3 to 12 | 13 to 26 | 30 |
| 8 banks | 1K Columns | 16K Rows | single rank |(31st address bit must be 0 all the time )
DDR4_Timing : {0 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,0, 0} /* CCD_L, CCD_S, RRD_L, RRD_S, WTR_L, WTR_S in ns */
(used only in DDR4 and DDR5)
DDR4:
In this configuration we are going to use 2400 data rate and a single channel 8 GB DDR4.
(1 clock preamble and 1KB page size)
Controller_Speed_MHz : 2400.0 (0.833e-9 clock time)
Burst_Length : 8 (8n prefetch)
Memory_Width_Bytes : 1 (x8 device)
Mfg_Suggest_Timing : 13.75, 13.75, 13.75, 32, 0, 13.3} /* tCL, tRCD, tRP, tRAS, tAL, tCWL in ns*/
Timing_Description:
CL - RCD - RP = 17 - 17 - 17
CL or AA = 17 clocks = 13.75ns
RCD =17 clocks = 13.75ns
RP =17 clocks = 13.75ns
RAS = 39 clocks = 32ns (RAS_min)
AL = 0 (choosing 0 additive latency, users choice)
CWL or WL = 16 clocks = 13.3ns
Extra_Timing : {0, 0, 0, 0, 15, 0, 7.5, 0, 21} /* DQSS, tWTR, tCCD, tRRD, tWR, tDQSCK, tRTP, tHWpre, tFAW in ns*/
Timing_Description:
DQSS min = 0.75 clock
DQSS max = 1.25 clock
we have to use 0 clock for all DDRs to maintain the same functionality, so 0ns
WTR = 0
CCD = 0
RRD = 0
WR = 15ns
DQSCK = 0
RTP = max(7.5ns, 4clk) = 7.5ns
HWpre = 0 (not used in the current version)
FAW = max(21ns,20clk) = 21ns
Memory_Column : {4,13}
Memory_Row : {14,29}
Memory_Bank : {0,3}
Memory_Rank : {30}
Address_Mapping:
16 banks - 4 bits to address it.(4 Bank groups and 4 banks per bank group)
1K Columns - 10 bits to address it
64K Rows - 16 bits to address it
Bank interleaved addressing format
| 0 to 3 | 4 to 13 | 14 to 29 | 30 |
| 16 banks | 1K Columns | 16K Rows | single rank |(31st address bit must be 0 all the time )
DDR4_Timing : {5.0,2.5,4.9,2.5,7.5,2.5} /* CCD_L, CCD_S, RRD_L, RRD_S, WTR_L, WTR_S in ns */
Timing_Description:
CCD_L = max(5ns, 4clk) = 5ns
CCD_S = 4clk = 2.5ns
RRD_L = max(4.9ns, 4clk)= 4.9ns
RRD_S = max(2.5ns, 4clk) = 2.5ns
WTR_L = max(7.5ns, 4clk) = 7.5ns
WTR_S = max(2.5ns, 2clk) = 2.5ns
| SDRAM Type | Size | Burst length | Memory Width Bytes | Data Rate | tCL | tRCD | tRP | tRAS | tAL | tCWL | DQSS | tWTR | tCCD | tRRD | tWR | tDQSCK | tRTP | tHWpre | tFAW | tCCD_L | tCCD_S | tRRD_L | tRRD_S | tWTR_L | tWTR_S | FGR | RFC | Retention Time |
| DDR3 1KB x8 | 2GB | 8 | 8 | 2133 | 13.09 | 13.09 | 13.09 | 33 | 0 | 9.37 | 0 | 7.5 | 3.75 | 3.75 | 15 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FGR_1x | 1.60E-07 | 6.40E-02 |
| DDR3 1KB x8 | 2GB | 8 | 8 | 1866 | 13.91 | 13.91 | 13.91 | 34 | 0 | 9.64 | 0 | 7.5 | 4.28 | 4.28 | 15 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 27 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FGR_1x | 1.60E-07 | 6.40E-02 |
| DDR3 1KB x8 | 2GB | 8 | 8 | 1600 | 13.75 | 13.75 | 13.75 | 35 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 7.5 | 5 | 5 | 15 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FGR_1x | 1.60E-07 | 6.40E-02 |
| DDR3 1KB x8 | 2GB | 8 | 8 | 1333 | 13.5 | 13.5 | 13.5 | 36 | 0 | 10.5 | 0 | 7.5 | 6 | 5 | 15 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FGR_1x | 1.60E-07 | 6.40E-02 |
| DDR3 1KB x8 | 2GB | 8 | 8 | 1066 | 13.125 | 13.125 | 13.125 | 37.5 | 0 | 11.25 | 0 | 7.5 | 10.25 | 5 | 15 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 37.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FGR_1x | 1.60E-07 | 6.40E-02 |
| DDR4 1KB x8 | 2GB | 8 | 8 | 3200 | 13.75 | 13.75 | 13.75 | 32 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 10 | 5 | 2.5 | 4.9 | 2.5 | 7.5 | 2.5 | FGR_1x | 1.60E-07 | 6.40E-02 |
| DDR4 1KB x8 | 2GB | 8 | 8 | 2933 | 14.32 | 14.32 | 14.32 | 32 | 0 | 10.91 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 10.87 | 5 | 2.72 | 4.9 | 2.5 | 7.5 | 2.5 | FGR_1x | 1.60E-07 | 6.40E-02 |
| DDR4 1KB x8 | 2GB | 8 | 8 | 2666 | 14.25 | 14.25 | 14.25 | 32 | 0 | 10.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 12 | 5 | 3 | 4.9 | 3 | 7.5 | 2.5 | FGR_1x | 1.60E-07 | 6.40E-02 |
| DDR4 1KB x8 | 2GB | 8 | 8 | 2400 | 14.16 | 14.16 | 14.16 | 32 | 0 | 9.99 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 13 | 5 | 3.33 | 4.9 | 3.3 | 7.5 | 2.5 | FGR_1x | 1.60E-07 | 6.40E-02 |
| DDR4 1KB x8 | 2GB | 8 | 8 | 2133 | 14.06 | 14.06 | 14.06 | 33 | 0 | 10.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 15 | 5.35 | 3.74 | 5.3 | 3.7 | 7.5 | 2.5 | FGR_1x | 1.60E-07 | 6.40E-02 |
| DDR4 1KB x8 | 2GB | 8 | 8 | 1866 | 13.92 | 13.92 | 13.92 | 34 | 0 | 10.71 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 17 | 5.35 | 4.28 | 5.3 | 4.2 | 7.5 | 2.5 | FGR_1x | 1.60E-07 | 6.40E-02 |
| LPDDR3 x32 | 8GB | 8 | 8 | 1600 | 15 | 18 | 18 | 42 | 0 | 7.5 | 1.25 | 7.5 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | FGR_1x | 3.50E-07 | 6.40E-02 |
| LPDDR5 | 8GB | 16 | 4 | 6400 | 6.5 | 18 | 18 | 42 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 34 | 0 | 7.5 | 0 | 20 | 5 | 2.5 | 5 | 5 | 12 | 6.25 | FGR_1x | 1.20E-07 | 3.20E-02 |
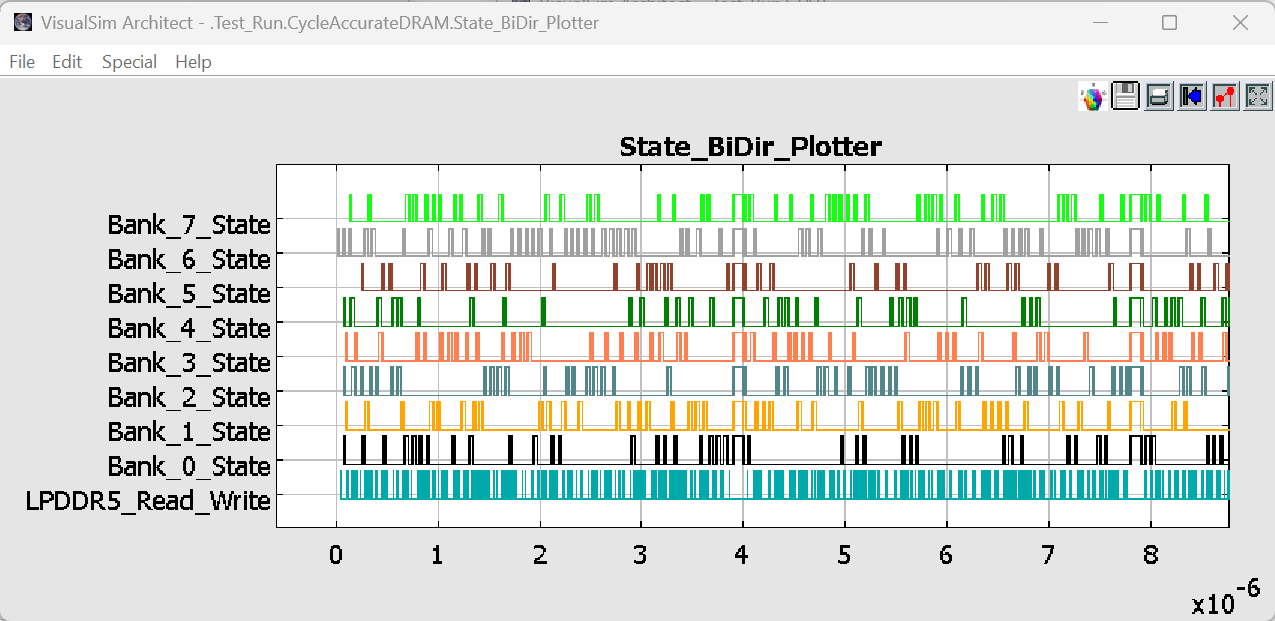
Enabling Plots
The internal transactions are analysed by the enabling Timing diagram in the model. Add the Timing Diagram block by (Hardware Setup -> TimingDiagram).Modify the Memory controler name and DRAM name in the Configuration window.
Below image shows the Timing Diagram for Memory controler and HWDRAM.
Power Configuration:
DRAM requires the following entries in
power table for power analysis. (Missing any of these entries will
cause an error):Format
1. ACT Stanby - "ACT_Stanby_"+DRAM_Name
2. ACT Active - "ACT_Active_"+DRAM_Name
3. Read Power - "Read_Power_"+DRAM_Name
4. Write Power - "Write_Power_"+DRAM_Name
5. Refresh Power - "RFSH_Power_"+Bank_ID+"_"DRAM_Name (Refresh power must be enterd for each bank, else an error will occur)
Example entries:
Architecture_Block Standby Active Wait Idle Existing OffState OnState t_OnOff Mhz Volts ;
1. ACT_Standby_DRAM 37.6 0.1 22.4 0.0 Standby Standby Active 0.0 1000.0 1.0 ;
2. ACT_Active_DRAM 37.6 0.1 22.4 0.0 Standby Standby Active 0.0 1000.0 1.0 ;
3. Write_Power_DRAM 0.0 216.2 0.0 0.0 Standby Standby Active 0.0 1000.0 1.0 ;
4. Read_Power_DRAM 0.0 392.2 0.0 0.0 Standby Standby Active 0.0 1000.0 1.0 ;
5. RFSH_Power_0_DRAM 11.8 12.0 0.0 0.0 Standby Standby Active 0.0 1000.0 1.0 ;
6. RFSH_Power_1_DRAM 11.8 12.0 0.0 0.0 Standby Standby Active 0.0 1000.0 1.0 ;
Note for Developer:
The refresh power supports only for 32 bank DRAM. If DRAM is configured beyond that the Refresh loops must be replicated to the required number of banks.
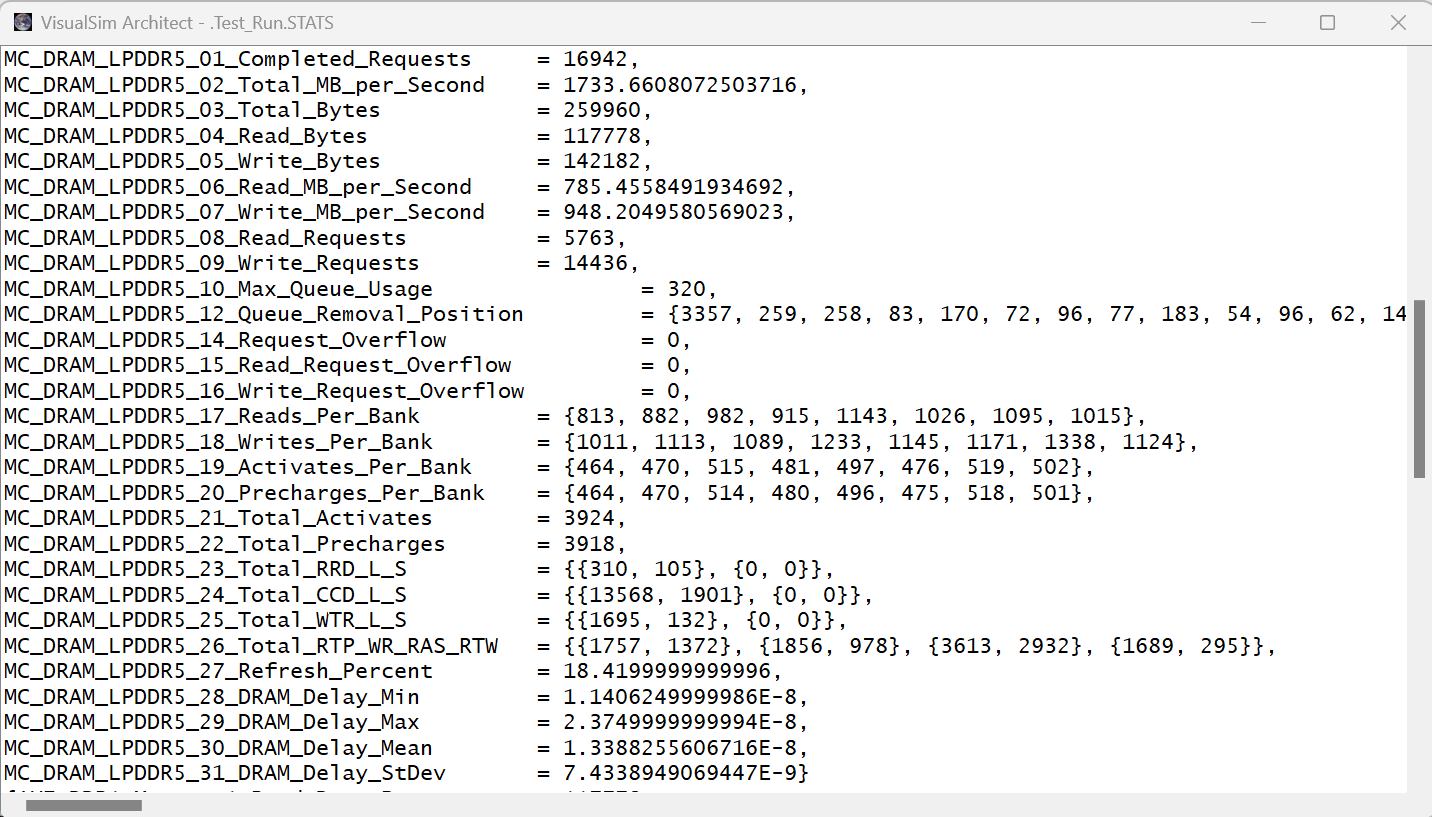
Statistics and Analysis
The mmory controller provides the following statistics that the user can observe and analyse the behabior of the block.1. Total_Requests:
Total number of input request reached the memory (both read and write)
2. Completed_Requests:
Total number of requests that are processed and completed by the memory.
3. Total_MB_per_Second:
Totoal throughput obtained by the memory for the simulated period.
4. Total_Bytes:
5. Read_Bytes:
6. Write_Bytes:
Total bytes processed by the memory for the simulated period.
7. Read_MB_per_Second:
8. Write_MB_per_Second:
Total throughput obtained by the memory for read and write request for the simulated period.
9. Read_Requests:
10. Write_Requests:
Total Read and write requests reached the memory.
11. Max_Queue_Usage: (Unified queue configuration)
11. Read_Queue_Max_Usage: (Split queue)
11.Write_Queue_Max_Usage: (Split queue)
The maximum buffer occupancy of the command queue in the simulated period. Max_Queue_Usage is for the unified buffer configuration. Read and Write max usage for the split queue configuration.
12.Queue_Removal_Position: (Unified queue configuration)
12.Read_Removal_Position: (Split queue)
12.Write_Removal_Position:(Split queue)
The removal positions of the queue that describes the effectiveness of the FR FCFS algorithm. the more removal of packets in the front end shows that arrival order is strictly maintained during the scheduling.
13. Request_Overflow: (Unified queue configuration)
14. Read_Request_Overflow: (Split queue)
15. Write_Request_Overflow: (Split queue)
The overflowed packets in unified queue and split queue.
16. Reads_Per_Bank:
17. Writes_Per_Bank:
The total requests per bank in an array format. This gives the traffic pattern insight according to the banks
18. Activates_Per_Bank:
Total number of activates per bank. it includes the activates activates following the refresh. Higher the number of activates reduces the bandwidth.
19. Precharges_Per_Bank:
Total number of precharges per bank. it includes the precharge before the start of refresh.
20. Total_Activates:
21. Total_Precharges:
Total number of activates and precharge in the entire memory.
22. Total_RRD_L_S
Total number of RRD timing constraints maintained in the execution. eg: {{12, 8},{30, 22}}.The 1st array list the total number of RRD_L and elapsed RRD_L. The second array list the total RRD_S and the elapsed RRD_S. DRAM type other than DDR4, DDR5 and LPDDR5 only show values in 1st array, second array will be {0,0}
23. Total_CCD_L_S
Total number of CCD timing constraints maintained in the execution. eg: {{12, 8},{30, 22}}.The 1st array list the total number of CCD_L and elapsed CCD_L. The second array list the total CCD_S and the elapsed CCD_S. DRAM type other than DDR4, DDR5 and LPDDR5 only show values in 1st array, second array will be {0,0}
24. Total_WTR_L_S
Total number of WTR timing constraints maintained in the execution. eg: {{12, 8},{30, 22}}.The 1st array list the total number of WTR_L and elapsed WTR_L. The second array list the total WTR_S and the elapsed WTR_S. DRAM type other than DDR4, DDR5 and LPDDR5 only show values in 1st array, second array will be {0,0}
25. Total_RTP_WR_RAS_RTW
A 2D array with each internal array shows the total number of actions for particualr timing constraint. In each subarray the 1st index shows the total number of occurance and the 2nd index shows the elapsed occurance. the order of the timing constraint are RTP, WR, RAS and RTW.
RTP will be {0,0} if no read request reached the memory. similarly WR will be {0,0} if no write reached the memory. RTW will be {0,0} if there is no combination of read and write in memory access.
26. Refresh_Percent
Total percent of time the refresh was active in the memory. Percentage in 100% format.
27. DRAM Delay: (Max, Mean, Min and Standard Deviation)
This shows the delay of DRAM memory access in min, max, mean and standard deviation
The following image shows the complete statistics of the block for an LPDDR4 DRAM.
Checklist before running the model:
- DRAM name and memory controller name are configured correctly in both blocks
- DRAM type must be same in memory controller and DRAM.
- Make sure the DRAM name is correctly configured with the appropriate source device.
- Make sure the timing parameters are configured as per
the data sheet from the vendor. The default values are for DDR4
obtained from micron datasheet.
- Memory_Width_Bytes must be same in memory controller and DRAM.
- Command_Buffer_Length must be either an integer or an array of integer with size 2. {Read,Write}
- Mfg_Suggest_Timing and Extra_Timing must be same in memory controller and DRAM.
- Memory_Coloumn, Memory_Row and Memory_Rank must be an array of integers.
- Memory_Coloumn, Memory_Row and Memory_Rank must match with the Address_Bit_Map parameter in DRAM.
- To enable power analysis, make sure the Power_Manager_Name is a valid name of Power Table. Power Table must have required entries of DRAM.
- Commands_in_a_Row parmeter must be an integer and less than or equal to command buffer length
- DRAM support single Bus interface, please make sure
all the packets are entered through that interface. Please don't
multiplex the signals through "Join" block.x
.
Deadlock and debugging:
Deadlock situations:- If Command_Buffer_Length is less than or equal to the total fragments of the input request the deadlock can occur.
- Fragments size = Burst_length * Memory_Width_Bytes, if input request size is greatrer than this size, it will fragmented.
- If TResolution is set to 1.0E-12 in Digital Simulator, it can cause a deadlock. Please reduce the TResolution to 1.0E-13.
Debugging methods:
- Enable Debug parameter in memory controller. Connect a text display to save or view the debug messages from memory controller.
- Look for last command issued to DRAM other than refresh messsages.
- Connect text display to ArchitectureSetup to observe statistics.
- Look for Total Requests and Completed_Requests.
- Enable State_Plot_Diagram in DRAM to observe the state of each bank in DRAM.
- Please make sure the ports are connected correctly. (output to input)
Error messages and Solutions
1.Error : Issue with RegEx execution
Exception :
VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException: Error invoking function
public static java.lang.String
VisualSim.data.expr.UtilityFunctions.throwMyException(java.lang.String) throws
VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException
Because:
User RegEx Exception:
SDRAM cannot locate Memory_Controller: none_Mem_Ctrl, suggest edit.
Please make sure the memory controler name is configured in the DRAM block.2.
Error : Issue with RegEx execution
Exception :
VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException: Error invoking function
public static java.lang.String
VisualSim.data.expr.UtilityFunctions.throwMyException(java.lang.String) throws
VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException
Because:
User RegEx Exception:
LPDDR_Mem_Ctrl DRAM_Type (DDR3) does
not match SDRAM DRAM_Type (DDR4), suggest edit.
3.
Error : Issue with RegEx execution
Exception :
VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException: Error invoking function
public static java.lang.String
VisualSim.data.expr.UtilityFunctions.throwMyException(java.lang.String) throws
VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException
Because:
User RegEx Exception:
LPDDR_Mem_Ctrl DRAM_Type (DDR3) does not match SDRAM DRAM_Type (none), suggest edit.
Please make sure the DRAM name is configured in the memory controller.
4.
Error : Issue with RegEx execution
Exception :
VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException: Error invoking function
public static java.lang.String
VisualSim.data.expr.UtilityFunctions.throwMyException(java.lang.String) throws
VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException
Because:
User RegEx Exception:
LPDDR_Address_Decoder input DS
missing a Field Name(s): {"A_Address"}
5.
VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException:
Block : Test_Run.Memory_Controller.Memory_Control
Error : Issue with RegEx execution
Exception : VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException: Error invoking function public static java.lang.String VisualSim.data.expr.UtilityFunctions.throwMyException(java.lang.String) throws VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException
Because:
User RegEx Exception:
'tCCD' timing doesnt match with the DRAM speed.
Please make sure the timings are configured as per the data sheet from the vendor.
Configured DRAM Data rate : 2400.0 and the tCCD : 5.0E-9
6.
VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException:
Block : Test_Run.Memory_Controller.Read_Data_from_Memory
Error : Issue with RegEx execution
Exception : VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException: Error invoking function public static java.lang.String VisualSim.data.expr.UtilityFunctions.throwMyException(java.lang.String) throws VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException
Because:
User RegEx Exception:
Parameter 'Mfg_Suggest_Timing', missing some values ={21.25, 18.0, 18.0, 43.0, 0.0}.
Expeceted Array size = 6.
Expected cycle Details and the order. eg:{tCL, tRCD, tRP, tRAS, tAL, tCWL}.
Please check the parameter configuration.
7.
VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException:
Block : Test_Run.Memory_Controller.Address_Decoder
Error : Issue with RegEx execution
Exception : VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException: Error invoking function public static java.lang.String VisualSim.data.expr.UtilityFunctions.throwMyException(java.lang.String) throws VisualSim.kernel.util.IllegalActionException
Because:
User RegEx Exception:
Input field 'A_Bytes' contains unsupported value =-12.
Value should be greater than 0. eg:8.
Future Implementations:
- Multi Rank Support: Timing constratint for multi rank activate and acces must be added
- LPDDR4 dual cycle issue: 2 cycle for issuing all the commands except precharge must be added
- All bank support for LPDDRs must be added.
- FAW constraint for activates following all bank refresh must be added.
- Postpone and Advance of refresh must be added.
- Gneralization of refresh code to support N banks must be added. Right now it support only 32 banks with hardcoded loops.
- Address bit map verification with the DRAM Size parameter can be added.
- Statistical Refresh support can be added.
- Row and Column boundary crossing as per the address bit map can be added.
- On multiple fragments the final packet will be considered only all the fragments are completed.